Detailed information
12
2025
-
09
Gain a deeper understanding of the operational principles of industrial control automation systems
As the "nervous system" of modern industrial production, industrial control automation systems achieve intelligent control of manufacturing processes through the seamless collaboration of three core components: sensing, decision-making, and execution. Integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines—including mechanical engineering, electronic technology, and computer science—these systems play an indispensable role in industries such as automotive manufacturing, petrochemicals, and power energy.
I. The Perception Layer: The "Digital Nerve" of the Industrial Site
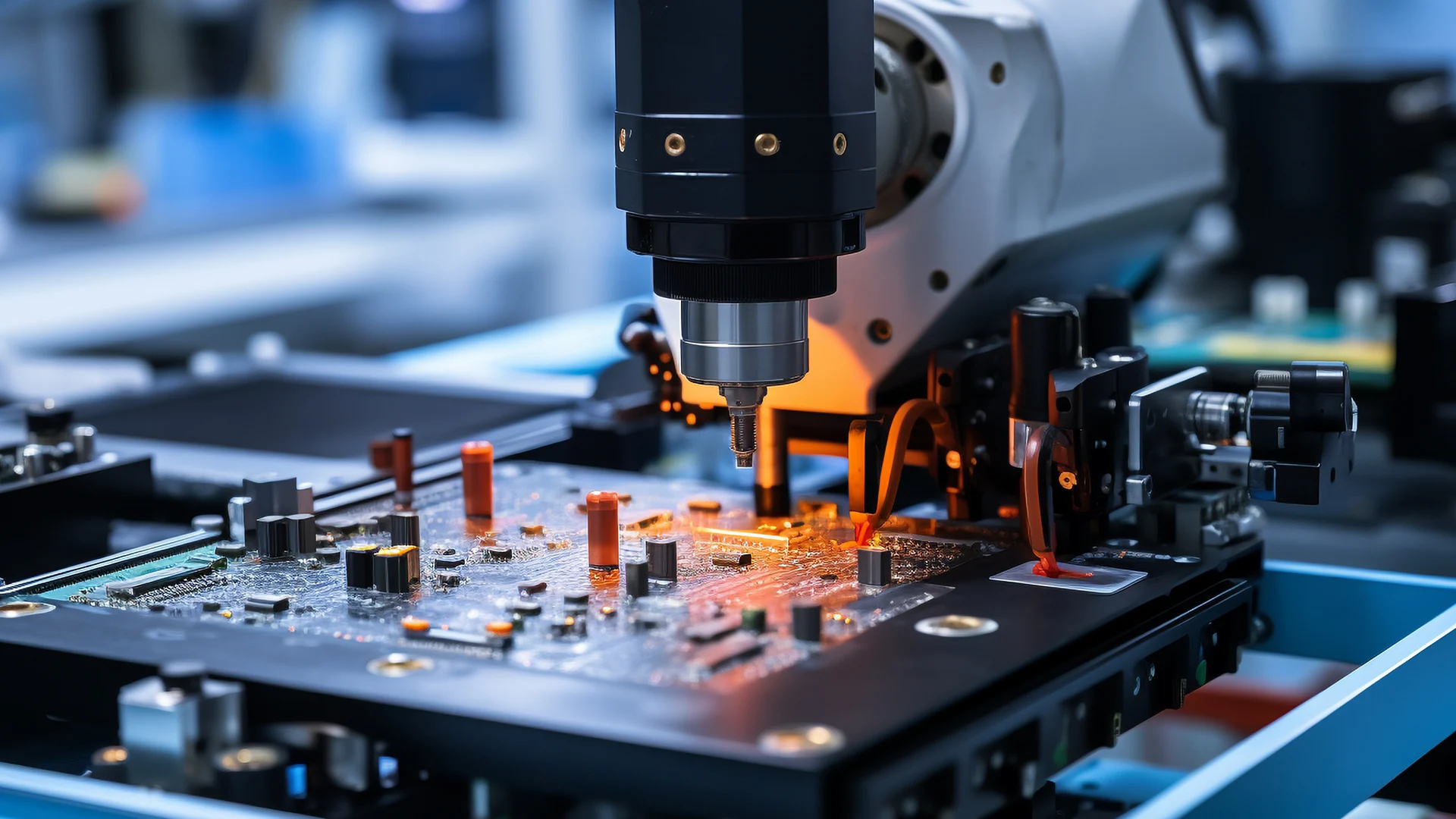
Sensor networks form the sensing foundation of industrial control systems, and their accuracy directly impacts control quality. Take, for example, an automotive assembly line: 3D laser sensors can achieve weld seam detection with precision down to 0.01 mm. By emitting laser beams and analyzing the reflected signals, these sensors precisely measure the assembly gaps between various vehicle body components. In the petrochemical industry, pressure transmitters convert fluid pressure within pipelines into a standard 4–20 mA electrical signal, while temperature sensors utilize PT100 platinum resistance technology, maintaining measurement accuracy of ±0.1°C across a wide temperature range from -200°C to 850°C.
Optoelectronic sensors demonstrate unique advantages in logistics sorting systems, detecting object presence by emitting infrared beams with response times as fast as 0.1 ms. At an e-commerce warehouse, an intelligent sorting system equipped with through-beam optoelectronic sensor arrays achieves precise sorting of up to 36,000 packages per hour, boasting an error rate below 0.001%. Meanwhile, inductive proximity switches play a critical role during tool-changing processes in CNC machine tools, accurately sensing changes in the electromagnetic properties of metal tools to ensure that clamping force exceeds 2,000 N, thereby preventing equipment malfunctions caused by tool loosening.
II. Decision-Making Layer: Intelligent Computing of the Industrial Brain
The Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), serving as the core decision-making unit, features a modular design that enables flexible configuration. The Siemens S7-1500 series PLC is equipped with a 1.8GHz quad-core processor, delivering an impressive processing speed of just 0.1μs per instruction, and supports 15 industrial protocols, including PROFINET and EtherCAT. In the painting workshop of a certain automotive plant, the PLC system collects data from over 2,000 I/O points in real time, precisely controlling the trajectories of spray robots to ensure uniform paint film thickness within a tolerance of ±2μm.
Distributed Control Systems (DCS) excel in the process industries. Honeywell’s Experion PKS system, featuring a dual-CPU hot-standby architecture, achieves system availability of up to 99.999%. At a certain refinery, the DCS system—equipped with a multivariable predictive control algorithm—reduced fluctuations in reaction temperature from ±5°C to just ±1.5°C, resulting in annual fuel cost savings exceeding 10 million yuan. Meanwhile, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are widely used in long-distance pipeline operations. Schneider’s EcoStruxure platform supports data collection from up to 100,000 points and enables seamless cross-system data exchange via the OPC UA protocol.
III. Execution Layer: Precision-Controlled Robotic Arm
The servo system forms the core power source of the execution layer. Yaskawa's Σ-7 series servo drives utilize fully digital control technology, achieving positioning accuracy as fine as ±0.001 mm. In semiconductor packaging equipment, a three-axis servo platform leverages encoder feedback to enable nanometer-level motion control, enabling chip mounting accuracy down to 2 μm. Meanwhile, pneumatic actuators are widely used in the food packaging industry. FESTO’s proportional valves, employing PWM modulation technology, precisely regulate compressed air pressure within the range of 0.05–0.8 MPa, ensuring that packaging bag sealing strength meets stringent quality standards.
Electric actuators excel in the field of valve control. AUMA electric heads feature a planetary gear reduction design, offering an output torque range from 10 to 20,000 Nm. In nuclear power plant cooling systems, electric control valves are operated via 4-20mA signals to precisely regulate opening degrees, with response times under 2 seconds—ensuring reactor temperatures remain stable within the critical range of 300±2°C. Meanwhile, hydraulic actuators are indispensable in heavy-duty machinery. For instance, Rexroth’s A4VG series piston pumps utilize variable control technology to achieve stepless displacement adjustment, boosting excavator boom arm movement speeds by up to 30%.
4. Communication Layer: The Lifeline of Industrial Networks
Industrial Ethernet establishes a high-speed data channel, and the EtherCAT protocol leverages time-division multiplexing technology to achieve synchronized control across 100 nodes with timing accuracy down to 100 microseconds. In a certain automotive factory’s welding workshop, more than 200 devices are interconnected via an EtherCAT network, enabling data transmission delays of less than 50 microseconds. Meanwhile, Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is emerging as a key technology in the automotive electronics sector, with Intel’s I210 network card supporting 802.1Qbv time-triggered communication, ensuring deterministic data transmission for ADAS systems.
Wireless communication technologies have expanded the boundaries of control. Wi-Fi 6 enables latency control as low as 50ms in AGV scheduling systems, while a smart warehouse deploys 200 AGVs connected via the 5GHz frequency band, achieving positioning accuracy within ±10mm. Meanwhile, LoRa technology excels in pipeline monitoring: a major oil and gas field has equipped 2,000 monitoring points with the LoRaWAN protocol, enabling low-power data transmission over distances of up to 10 km—and ensuring battery life lasting up to 5 years.
5. System Integration: Innovative Practices Through the Fusion of Multiple Technologies
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platform is driving device connectivity, with Siemens' MindSphere platform already connecting over 30 million devices. By leveraging edge computing for data preprocessing, it helps reduce the load on cloud infrastructure. For instance, a steel company’s hot-rolling production line successfully integrated 500 smart gateways, enabling seamless communication among PLCs, sensors, and cameras—and boosting fault prediction accuracy to 85%. Meanwhile, digital twin technology is widely adopted in the aerospace industry; Airbus, for example, uses Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE platform to create a comprehensive digital model of its entire aircraft, cutting the aerodynamic design cycle by 40%.
Artificial intelligence is powering control optimization—specifically, a chemical plant’s cracking furnace now leverages a deep learning model. By analyzing 10 years of historical data, the plant has boosted ethylene yield by 1.2 percentage points, resulting in annual revenue gains exceeding 10 million yuan. Meanwhile, in the wind energy sector, Goldwind Science & Technology has implemented a predictive maintenance system that uses LSTM neural networks to analyze vibration data, enabling it to predict gearbox failures up to 72 hours in advance—and reducing unplanned downtime by 60%.
Industrial automation systems are evolving toward openness and intelligence, with OPC UA leading the way.
Keywords:
Servo drive
Qifan