Detailed information
12
2025
-
09
Technical Analysis and Application Cases of High-Power Servo Drives
In the future, as the OPC UA over TSN industrial communication protocol gains wider adoption, servo drives will facilitate millisecond-level data exchange with PLCs and vision systems, propelling toward a more autonomous phase marked by "self-sensing, self-decision-making, and self-execution."
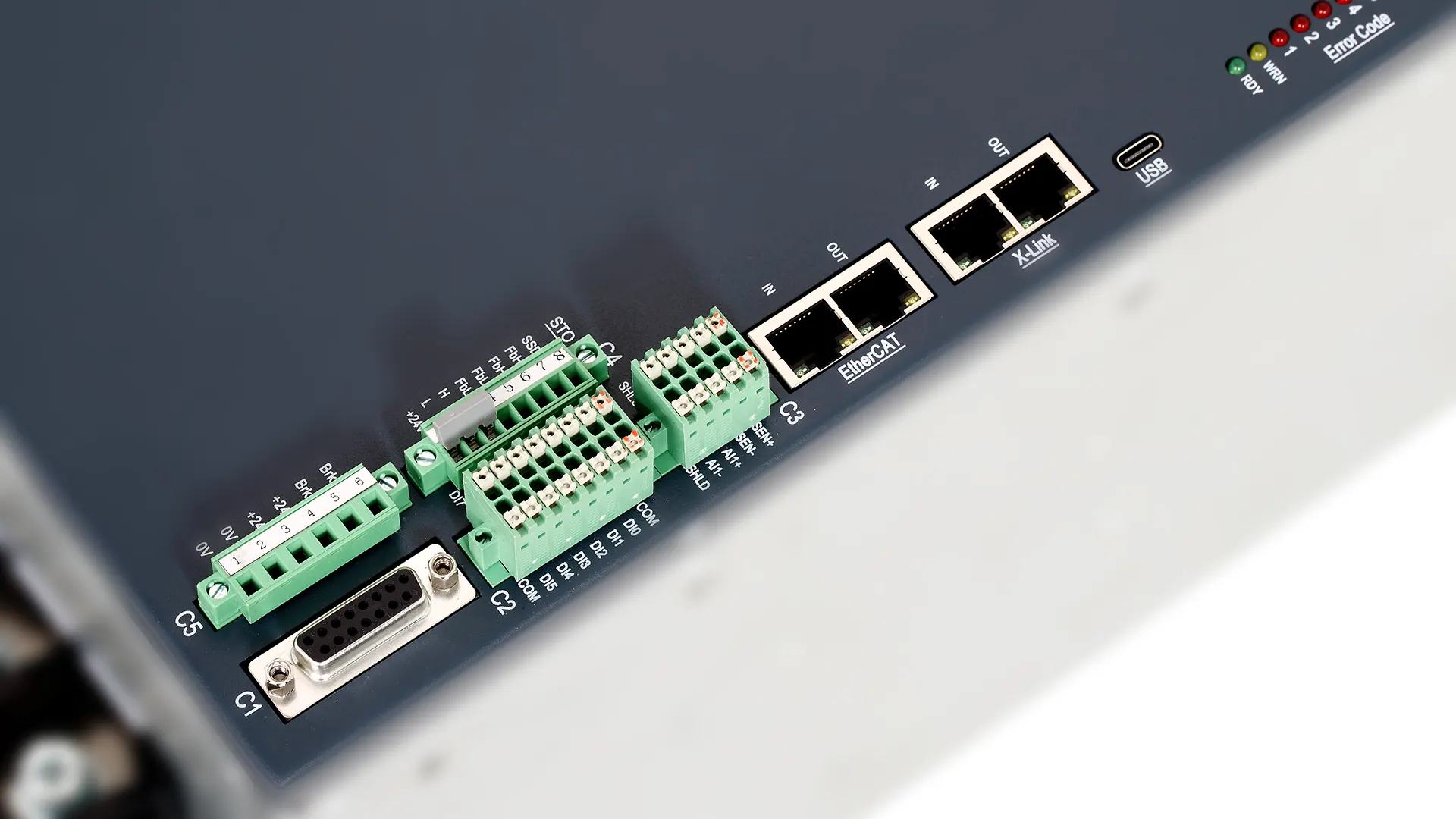
As a core component of industrial automation, high-power servo drives rely on the deep integration of power electronics and advanced control algorithms to precisely regulate motor torque, speed, and position. Take the DS5 series high-power servo drives as an example—ranging from 11 kW to 15 kW in power output—they feature a three-phase full-wave rectified IPM module combined with PWM control technology, enabling efficient motor operation via sinusoidal current drive.
At the control algorithm level, mainstream products typically adopt the vector control principle to build a three-loop control system encompassing current, speed, and position. Among these, the dynamic response capability of the speed loop directly determines the overall system performance. For instance, the DS5 series leverages high-resolution 17-bit/23-bit encoders for position feedback, combined with a feedforward compensation algorithm, enabling it to achieve positioning accuracy as fine as 1 command unit—significantly enhancing the precision of width setting—even during high-speed motion, while still maintaining micron-level accuracy in positioning.
II. Hardware Architecture: Balancing Integration and Reliability
The hardware design of high-power servo drives must balance power density with operational stability. Take the DS5K1-411P0 model as an example: it features a compact structural design, reducing its size by 32% compared to the previous generation. Yet, thanks to the combination of a built-in braking unit and an external braking resistor, it still delivers up to 15 kW of power output. Key technological breakthroughs include:
1. **Power Module Integration**: Utilizing an IPM intelligent power module that integrates driver circuits along with 12 protection features—including overvoltage, undervoltage, and overheating—reducing fault response time to within 10μs.
2. **Multi-Communication Interface Compatibility**: Supports RS232, RS485, and EtherCAT bus communication, enabling control of up to 32 axes in synchronized motion—perfect for meeting the collaborative demands of complex production lines.
3. **Optimized Environmental Adaptability**: The operating temperature range has been extended to -10°C to 40°C, with humidity tolerance up to 90% RH, enabling the device to perform reliably in harsh conditions such as metal cutting and new energy equipment applications.
III. Analysis of Typical Application Scenarios
1. CNC Machines: Ensuring Precision in High-Speed Cutting
In the field of metal cutting, Mitsubishi’s MR-JE series drives support spindle speeds of up to 20,000 rpm and, when paired with grating-scale closed-loop control, enable aerospace engine blade machining with an accuracy of ±0.001 mm. Additionally, the drive boasts a dynamic response bandwidth of up to 500 Hz, allowing it to accelerate from standstill to its rated speed in as little as 0.1 seconds—significantly boosting machining efficiency.
2. New Energy Equipment: Precision Control Through Multi-Axis Synchronization
On the lithium-battery production line, Inovance’s IS620N series drives ensure precise alignment of electrode sheets in the winding machine, thanks to a synchronized tension-control algorithm that keeps the alignment error below ±0.05 mm. Meanwhile, in photovoltaic string welding machines, ESTUN drives paired with linear motors enable micrometer-level adjustments, achieving solar cell welding positioning accuracy as fine as ±0.02 mm—and significantly reducing breakage rates.
3. Industrial Robots: Stable Drive for High-Dynamic Loads
The Yaskawa Electric Sigma-7 series drives excel in automotive welding robots, delivering a remarkable 1ms response delay and boasting a 200% overload capacity, enabling precise control of six-axis robotic arms for spot welding tasks with accuracy down to 0.1mm. Meanwhile, in the collaborative robotics space, Universal Robots' UR series leverages torque-mode control to achieve flexible force feedback during human-robot collaboration, with collision detection response times reduced to as low as 2ms—ensuring enhanced operational safety.
4. Packaging Logistics: The Efficiency Revolution of Flexible Production Lines
The L7 series drives from Rays Intelligent achieve a 0.1-second response time in express sorting systems, enabling multi-axis coordinated control with cross-belt sorters and boosting throughput to over 12,000 items per hour. Meanwhile, in the food packaging sector, Schneider’s Lexium series utilizes analog torque control to maintain filling accuracy within a tight margin of ±1 ml, meeting the stringent requirements of industries such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products.
IV. Technical Challenges and Development Trends
Currently, high-power servo drives face three major challenges:
1. **Integration Bottleneck**: As robots move toward miniaturization, drives must achieve higher power density within limited space, making the application of GaN power devices a crucial breakthrough.
2. **Intelligent Upgrade**: The AI-based adaptive control algorithm optimizes control parameters in real time, such as predicting load changes through machine learning, thereby increasing system efficiency by more than 15%.
3. **Greening Requirements**: By incorporating silicon carbide MOSFETs and dynamic braking resistor technology, the drive can reduce energy consumption by 20%, meeting the EU's ERP energy efficiency standards.
In the future, as the OPC UA over TSN industrial communication protocol becomes more widespread, servo drives will enable millisecond-level data exchange with PLCs and vision systems, driving智能制造 toward a more autonomous phase characterized by "self-sensing, self-decision-making, and self-execution."
Keywords:
Servo drive
Qifan